The Always-On Display (AOD) is a signature feature of Samsung Galaxy phones with AMOLED screens, allowing users to glance at essential information like time, date, notifications, and battery status without fully waking up their device. But AOD is not just about utility; it’s also a canvas for personalization. Modern Samsung devices, especially those running recent versions of One UI, offer a surprising depth of customization, including the ability to add animations, GIFs, and dynamic visual elements to your AOD, making your phone truly unique.
The Always-On Display was first introduced by Samsung with the Galaxy S7 in 2016. Its core principle relies on the power efficiency of AMOLED technology, where individual pixels can be turned off completely to display true black, meaning only the illuminated pixels consume power. This makes it possible to show information continuously with minimal battery drain, unlike LCD screens which would require the entire backlight to be on. Over the years, Samsung has significantly expanded AOD’s capabilities, moving beyond simple clocks to incorporate complex designs, custom images, and, notably, animations to cater to users’ desire for expressive phone interfaces.
Understanding Animated AOD Options
Samsung offers several ways to integrate animation into your Always-On Display. These primarily fall into a few categories:
- Pre-loaded Animated AODs: Samsung provides a selection of built-in animated clock styles and designs.
- GIFs from Gallery: You can choose a short GIF from your phone’s gallery to display on the AOD.
- Animated AOD Themes: The Galaxy Themes store offers various animated AOD themes, some free and some paid.
- Good Lock Modules (ClockFace/LockStar): For advanced customization, Samsung’s Good Lock app, particularly its ClockFace or LockStar modules, provides unparalleled control over AOD animations and elements.
It’s important to note that animated AODs, while visually appealing, will consume slightly more battery than static ones because more pixels are actively changing or illuminated.
How to Customize Your Samsung AOD with Animations (Standard Methods)
These methods use the built-in settings found on most compatible Samsung Galaxy phones.
Method 1: Using Pre-loaded Animated AOD Styles
- Go to Settings:
- Swipe down from the top of your screen to open the Quick Settings panel, then tap the gear icon (Settings).
- Alternatively, find and tap the Settings app icon in your app drawer.
- Navigate to Lock screen and AOD:
- Scroll down and tap on “Lock screen and AOD” (or just “Lock screen” on some older versions).
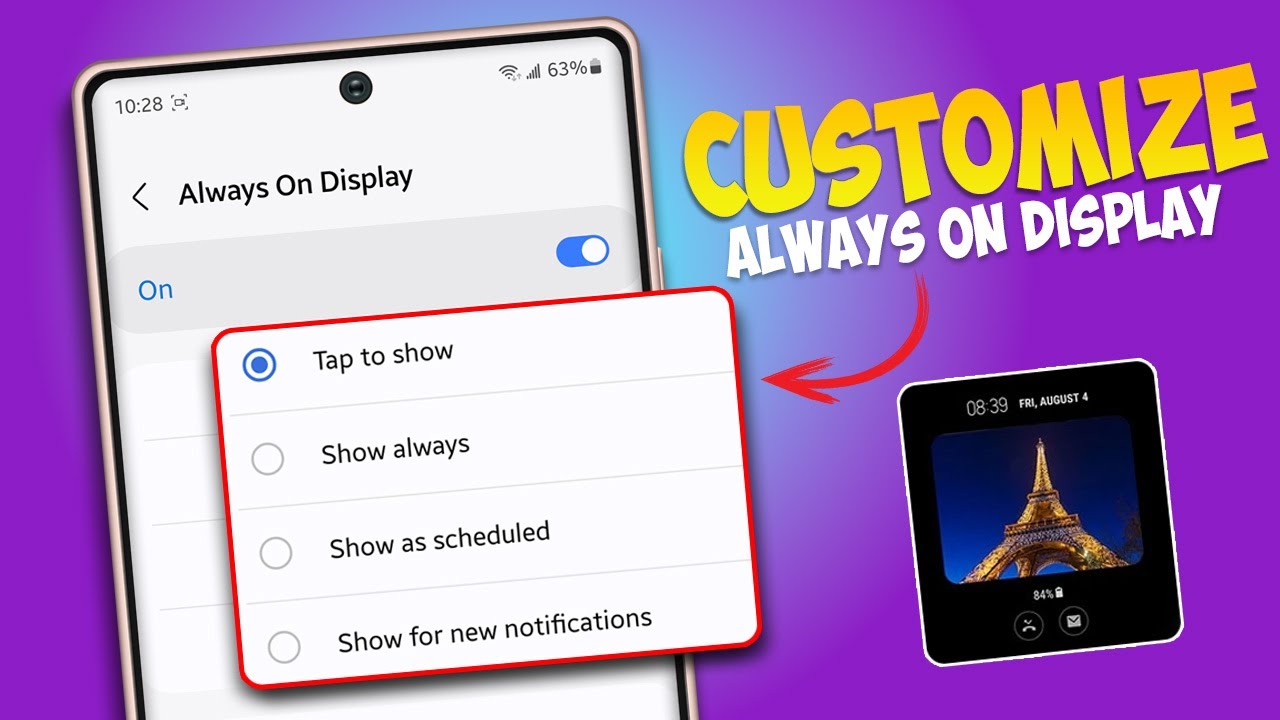
- Enable Always On Display:
- Ensure the “Always On Display” toggle is ON. Tap on the “Always On Display” text itself (not just the toggle) to enter its detailed settings.
- Entity Definition: AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) is a type of display technology used in many modern smartphones, including Samsung Galaxy devices. Unlike LCDs, AMOLED pixels generate their own light, allowing for true blacks and vibrant colors, and enabling features like Always-On Display as individual pixels can be turned off.
- Select Clock Style:
- Tap on “Clock style.”
- Browse Animated Options:
- Within the “Clock style” menu, you’ll see various clock types (digital, analog, calendar, etc.). Look for tabs or sections that specifically show “Image clock,” “GIF,” or “Animated AODs.”
- Swipe through the available pre-loaded animated options. These often include abstract patterns, simple character animations, or dynamic gradients.
- Apply Your Choice:
- Select the animated style you prefer and tap “Done” or “Apply.”
Method 2: Adding a GIF from Your Gallery
This is a popular way to personalize your AOD with custom animations.
- Follow Steps 1-4 from Method 1 (Settings > Lock screen and AOD > Always On Display > Clock style).
- Tap on the “Image” or “GIF” Tab/Icon:
- In the “Clock style” menu, you’ll typically see an icon that looks like a landscape photo or a GIF icon. Tap this.
- Select a GIF from Gallery:
- Tap the “+” icon (Add GIF) or choose “Gallery” to browse your phone’s stored GIFs.
- Important Note: For optimal performance and battery life, AOD GIFs are usually limited in length (e.g., typically 5-6 seconds or less). If your GIF is longer, the phone might only play a portion of it once or loop it twice depending on the length. The system will likely warn you about this.
- Adjust and Apply:
- You might be able to crop the GIF or select a specific segment.
- Tap “Done” or “Apply.” Your chosen GIF will now play on your AOD when the screen is off.
Method 3: Downloading Animated AOD Themes from Galaxy Themes
Samsung’s Galaxy Themes store is a rich source of customization, including animated AODs.
- Open Galaxy Themes:
- Long-press on an empty spot on your home screen.
- Tap “Themes” from the bottom menu.
- Alternatively, find the “Galaxy Themes” app in your app drawer.
- Navigate to AODs:
- Within the Galaxy Themes app, look for a tab or section specifically for “AODs” or “Always On Displays.”
- Browse and Download:
- Browse through the available animated AOD themes. Many will have a small “play” icon or a preview to indicate animation.
- Select a theme you like. Check if it’s free or paid.
- Tap “Download.”
- Apply the Theme:
- Once downloaded, tap “Apply.”
- You might be asked if you want to apply the “Clock and image” or “Image only” style. Choose your preference and tap “Done.”
- To manage downloaded AODs later, go to Galaxy Themes > Menu (three lines) > My stuff > AODs.
Advanced Customization with Samsung Good Lock (ClockFace / LockStar)
For the most extensive control over AOD animations and design, Good Lock is indispensable.
- Entity Definition: Good Lock is a suite of powerful customization modules developed by Samsung for its Galaxy devices. Available on the Galaxy Store, it allows users to deeply personalize various aspects of One UI, including the lock screen, quick panel, recent apps, and the Always-On Display.
- Entity Definition: One UI is Samsung’s customized Android user interface that runs on its Galaxy smartphones and tablets. It’s designed for easier one-handed use and offers a clean, intuitive design with extensive customization options.
- Download Good Lock:
- Open the Galaxy Store.
- Search for “Good Lock” and install it.
- Install ClockFace (or LockStar):
- Open the Good Lock app.
- Within Good Lock, find and tap on the “ClockFace” module (or “LockStar” on some versions/updates, as AOD customization is sometimes integrated there). Download and install it.
- Open ClockFace/LockStar:
- Once installed, tap on ClockFace (or LockStar) from within the Good Lock app to open it.
- Create or Select an AOD Style:
- ClockFace: You’ll see various pre-made clock styles, or you can tap the “+” icon to create your own custom AOD. Here, you’ll find options to:
- Add animated stickers.
- Integrate your own GIFs more seamlessly.
- Customize the clock’s font, size, and color.
- Add various visual elements.
- LockStar: If AOD customization is under LockStar, you’ll be able to edit both your lock screen and AOD layout, adding and repositioning clocks, widgets, and images/animations.
- ClockFace: You’ll see various pre-made clock styles, or you can tap the “+” icon to create your own custom AOD. Here, you’ll find options to:
- Add Animations/GIFs:
- Within the ClockFace editor (or LockStar’s AOD editing interface), look for options to add “stickers,” “images,” or “GIFs.”
- You can often layer multiple elements, including animated ones, to create a truly unique AOD.
- Apply Your Custom AOD:
- After designing your AOD, tap “Apply” or “Save” to set it as your Always-On Display.
Important Considerations
- Battery Consumption: Animations and complex AOD designs consume more battery than simple, static clocks. If battery life is a critical concern, choose simpler AODs or set it to “Tap to show” or “Show for new notifications.”
- Screen Burn-in: While AMOLED screens are susceptible to screen burn-in, Samsung intelligently mitigates this risk on AOD by subtly shifting the displayed elements around the screen over time. Animated elements are also designed with this in mind.
- Device Compatibility: Always-On Display and its advanced customization options are generally available on Samsung Galaxy phones with AMOLED screens, typically starting from the Galaxy S7 and newer flagship and mid-range devices. Older models or those with LCD screens will not support AOD.
- One UI Version: The exact steps and available options might vary slightly depending on your phone’s One UI version. Samsung frequently updates and refines these features.
By leveraging the built-in settings and powerful tools like Good Lock, you can transform your Samsung Galaxy’s Always-On Display from a mere utility into a dynamic and personalized extension of your phone’s unique style, complete with engaging animations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is Samsung Always-On Display (AOD)?
A1: Always-On Display (AOD) is a feature on Samsung Galaxy phones (and other phones with AMOLED screens) that allows a portion of the screen to remain active, displaying essential information like the time, date, battery level, and notifications, even when the rest of the screen is off. It provides quick access to information without needing to fully wake up your phone.
Q2: Do animated AODs drain more battery than static ones?
A2: Yes, animated AODs generally consume slightly more battery than static ones. This is because animations require more pixels to be actively changing and illuminated, leading to increased power consumption compared to a static clock or image where fewer pixels are consistently active.
Q3: Can I use any GIF from my gallery as an AOD animation?
A3: You can use GIFs from your gallery, but there are often limitations. Samsung’s AOD is optimized for short GIFs (typically under 5-6 seconds). Longer GIFs may only play a portion of the animation once or loop a couple of times before becoming static to conserve battery and prevent excessive processing.
Q4: What is Samsung Good Lock and how does it help with AOD customization?
A4: Good Lock is a suite of official Samsung apps available in the Galaxy Store that provides extensive customization options for One UI. For AOD, its ClockFace (or sometimes integrated into LockStar) module allows users to create highly personalized AOD designs, including adding custom animated stickers, GIFs, changing clock styles, fonts, and colors beyond what’s available in the standard settings.
Q5: Will using AOD cause screen burn-in on my Samsung phone?
A5: While AMOLED screens are theoretically susceptible to screen burn-in (permanent discoloration from static images), Samsung’s Always-On Display is designed to prevent this. The displayed elements (like the clock and notifications) are constantly and subtly shifted by a few pixels over time, preventing any single pixel from being illuminated for too long and significantly mitigating the risk of burn-in.
Q6: Why can’t I find the Always-On Display option on my Samsung phone?
A6: If you can’t find the Always-On Display option, it’s likely due to one of these reasons:
- Your phone model does not have an AMOLED screen. AOD is primarily supported by devices with AMOLED panels.
- Your phone’s software is outdated. Ensure your One UI is updated to the latest version.
- Power saving mode is enabled. AOD is automatically disabled when power saving mode is active to conserve battery. Disable power saving mode to enable AOD.